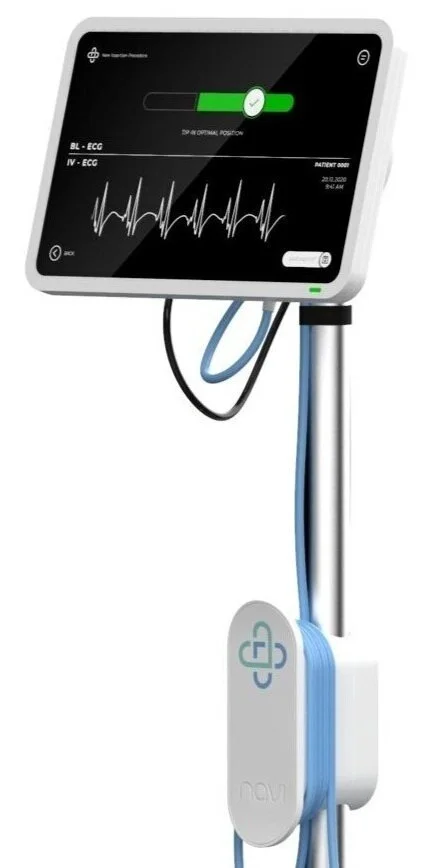
The Neonav® ECG Tip Location System
Navi Medical Technologies is focused on developing innovative pediatric medical devices that enable children to live brighter, healthier futures.
The Neonav® ECG Tip Location System is currently under development with this vision in mind, and will enable clinical staff to provide faster, more cost effective care that ultimately leads to better patient safety and improved outcomes for children around the world.
Please note: The Neonav® is still in development and is not yet approved for sale.
The Neonav ECG Tip Location System
*concept design render
Navi Medical Technologies is focused on developing innovative paediatric medical devices that enable children to live brighter, healthier futures.
The Neonav ECG Tip Location System is currently under development with this vision in mind, and will enable clinical staff to provide faster, more cost effective care that ultimately leads to better patient safety and improved outcomes for children around the world.
*Product concept render
Reduced patient risks
The Neonav could improve patient safety by increasing the number of 'first time right' insertion attempts, minimising exposure to ionising radiation, avoiding complications arrising from undiagnosed catheter migration.
Children (and in pre-term newborns in particular) admitted to the ICU are often exposed to ionising radiation which can lead to greater lifetime risks of cancer (1)(2)(3). Some centres perform regular X-rays to check for undiagnosed catheter tip migration(4). ECG Tip Location Systems have been shown to avoid the need for confirmatory X-rays(5) in adults. The Neonav is being designed to assess tip location in children during insertion, as well as post-insertion to check for migration without exposing the patient to additional X-rays.
Misplaced or migrated central lines are associated with higher incidences of serious complications including cardiac tamponade(5), hepatic extravasation(7) and thrombus formation(6). The Neonav can improve patient safety by enabling clinicians to re-assess the position of the central line in order to avoid some of the potential complications associated with catheter tip migration.
References:
1 - Kutanzi KR, Lumen A, Koturbash I, Miousse IR. Pediatric Exposures to Ionizing Radiation: Carcinogenic Considerations. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13(11):1057. Published 2016 Oct 28. doi:10.3390/ijerph13111057
2 - Baird R, Tessier R, Guilbault MP, Puligandla P, Saint-Martin C. Imaging, radiation exposure, and attributable cancer risk for neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 2013 May;48(5):1000-1005. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.02.016.
3 - Kartikeswar GAP, Parikh TB, Pandya D, Pandit A. Ionizing Radiation Exposure in NICU. Indian J Pediatr. 2020;87(2):158-160. doi:10.1007/s12098-019-03126-9
4 - Hoellering, A., Tshamala, D. and Davies, M.W. (2018), Study of movement of umbilical venous catheters over time. J Paediatr Child Health, 54: 1329-1335. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.14073
5 - Hou et al, 2020, Pericardial Effusion/Cardiac Tamponade Induced by Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Case Report and Literature Review, Frontiers in Pediatrics
6 - Shahroor et al 2020, Complications Associated with Low Position versus Good Position Umbilical Venous Catheters in Neonates of <32 Weeks’ Gestation, American Journal of Pediatrics
7 - Hanrahan et al, 2013, Hyaluronidase for treatment of intravenous extravasations: implementation of an evidence-based guideline in a pediatric population, J Spec Ped Nursing
CLINICAL BENEFITS
The ability to confirm catheter tip location in real-time may lead to faster procedures, higher numbers of 'first time right' placement procedures, and improved clinician confidence.
The use of ECG Tip Location Systems in adult procedures has also been shown to increase the porportion of well-placed insertion attempts(2). The Neonav is expected to offer similar levels of performance in the pediatric population, and improve the number of 'first time right' procedures in the NICU & PICU setting.
Improving the clinical workflow by enabling faster and easier procedures can lead to higher confidence and satisfaction in clinicians by removing frustration and providing the peace-of-mind that patients are receiving the best possible care.
References:
1 - NICE Medical Technologies Guidance, 25 March 2015. The Sherlock 3CG Tip Confirmation System for placement of peripherally inserted central catheters.
2 – Barton, Confirming PICC tip position during insertion with real-time information, BJNursing, 2016
ECONOMIC BENEFITS
The Neonav may lead to lower costs of care by avoiding additional procedures to correct misplacements, improving clinical workflow, reducing the number of X-rays required to confirm tip placement, and by avoiding the risks of complications associated with migrated central lines.
Undiagnosed migration of central lines occurs frequently, and migrated (or non-central) lines are associated with elevated risks of complications including cardiac tamponade, hepatic extravasation and thrombus formation(2). These complciations can be costly to treat, and expose hospitals to significant medico-legal risks. The Neonav offers the ability to perform routine checks to verify the position of the catheter tip during treatment, which may reduce the occurence of undiagnosed migration and therefore reduce the number of complications and minimise legal risks.
References:
1 - NICE Medical Technologies Guidance, 25 March 2015. The Sherlock 3CG Tip Confirmation System for placement of peripherally inserted central catheters.
2 – Hoellering et al, Study of movement of umbilical venous catheters over time , JPed & Child Health 2018